Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 The Transport Museum NCERT Solutions
Chapter 13 – “The Transport Museum” from Class 4 Maths takes students on an exciting journey through different types of old and new vehicles. While exploring the museum, students solve interesting puzzles, use numbers, and understand time, distance, and patterns in a fun way. This chapter helps build logical thinking and observation skills through real-life examples. In this post, you will find clear and easy-to-understand solutions to all the exercises from this chapter to support your learning and revision.
Textbook Page 184
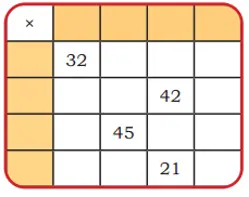
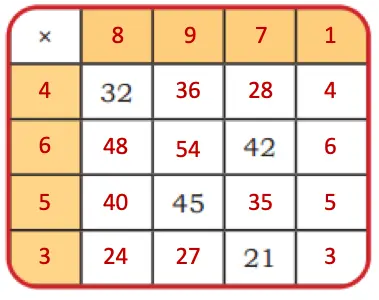
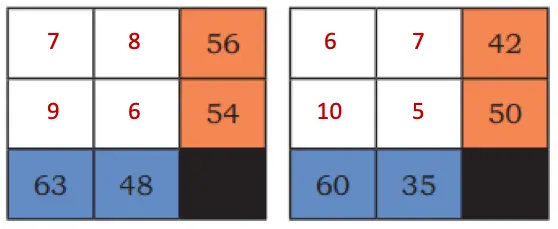
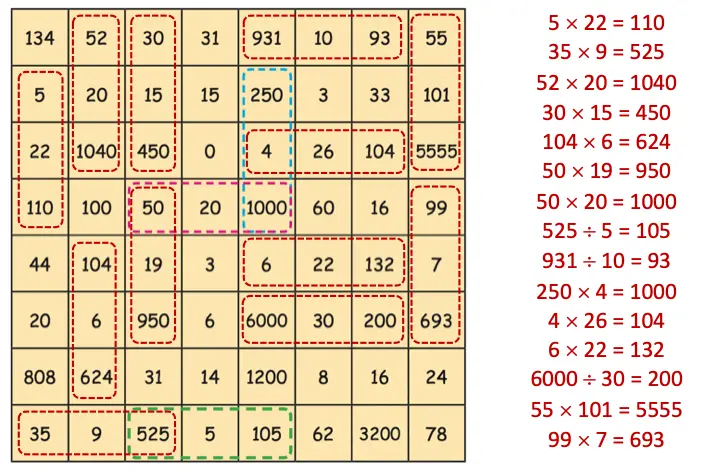
Mystery Matrix
Q. Fill the yellow boxes with 1-digit numbers (multiplicands and multipliers) such that you get the products given in the white boxes.
Fill the remaining white boxes with appropriate products.
Solution:
Q. The product of the numbers in each row is given in the orange boxes. The product of the numbers in each column is given in the blue boxes. Identify appropriate numbers to fill the blank boxes.
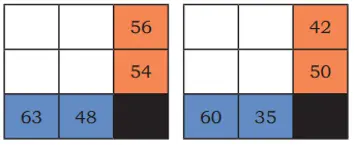
Solution:
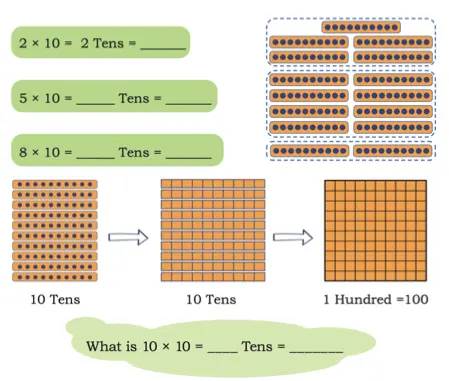
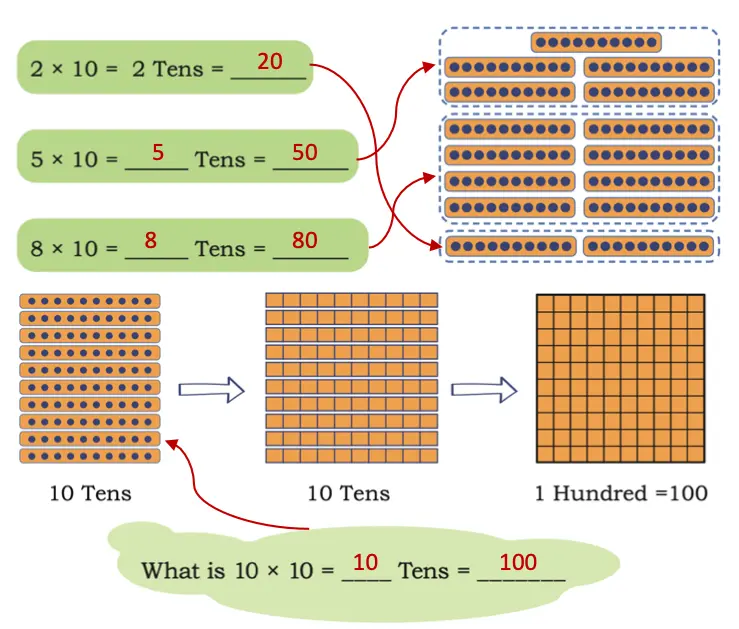
Times 10
Q. Match each problem with the appropriate pictorial representation and write the answer.
Solution:
Textbook Page 185
Constructing Tables
Q. How many pebbles are there in this arrangement? _______

Solution:
Pebbles = 5 × 15 = 75.
Q. This is a 5 × 15 arrangement. There is an easy way to find this product by splitting the arrangement.
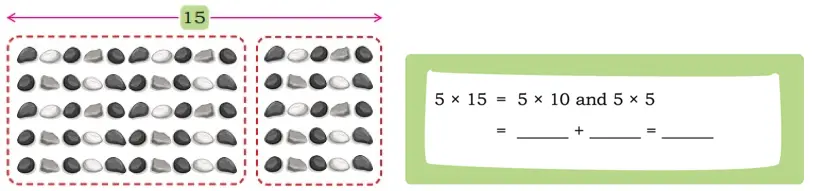
Solution:
5 × 15 = 5 × 10 and 5 × 5 = 50 + 25 = 75.
Textbook Page 186
Q. Recall the times-tables that we created in Grade 3. Now construct a times-15 table. You may use the arrangement given below and split the columns into 10 and 5 for ease of counting, as shown on the previous page.
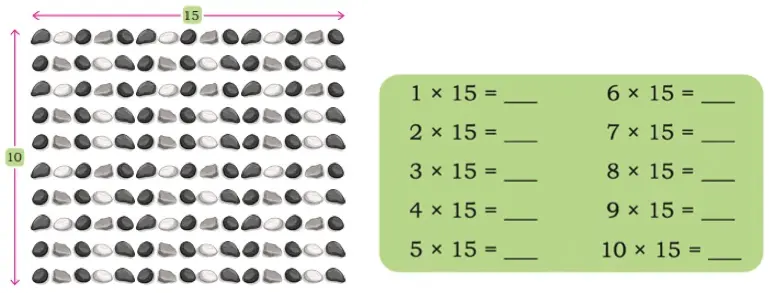
Solution:
1 × 15 = 1 × 10 and 1 × 5 = 10 + 5 = 15.
2 × 15 = 2 × 10 and 2 × 5 = 20 + 10 = 30.
3 × 15 = 3 × 10 and 3 × 5 = 30 + 15 = 45.
4 × 15 = 4 × 10 and 4 × 5 = 40 + 20 = 60.
5 × 15 = 5 × 10 and 5 × 5 = 50 + 25 = 75.
6 × 15 = 6 × 10 and 6 × 5 = 60 + 30 = 90.
7 × 15 = 7 × 10 and 7 × 5 = 70 + 35 = 105.
8 × 15 = 8 × 10 and 8 × 5 = 80 + 40 = 120.
9 × 15 = 9 × 10 and 9 × 5 = 90 + 45 = 135.
10 × 15 = 10 × 10 and 10 × 5 = 100 + 50 = 150.
1. What patterns do you see in this table?
Solution:
(i) Each number in the table increases by 15. Example: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, …
(ii) All the numbers are multiples of 5.
(iii) All the numbers end in either 0 or 5.
2. Compare the times-15 table with the times-5 table. What similarities and differences do you notice?
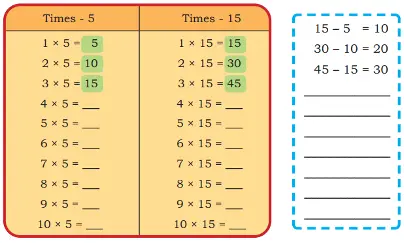
Solution:
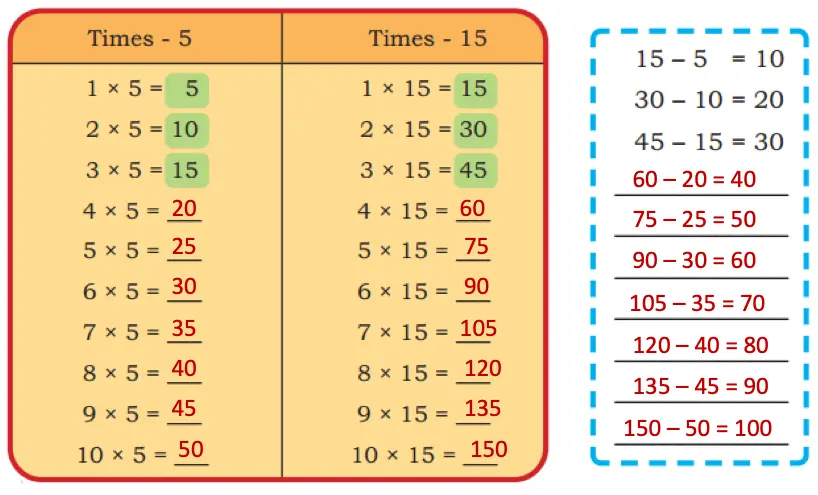
Similarities:
(i) Both are multiples of 5 and end in 0 or 5.
(ii) Both tables have odd and even numbers in alternate positions.
Differences:
(i) Numbers in the times-15 table increase by 15, while numbers in the times-5 table increase by 5.
(ii) Every number in the times-15 table appears in the times-5 table, but not vice versa.
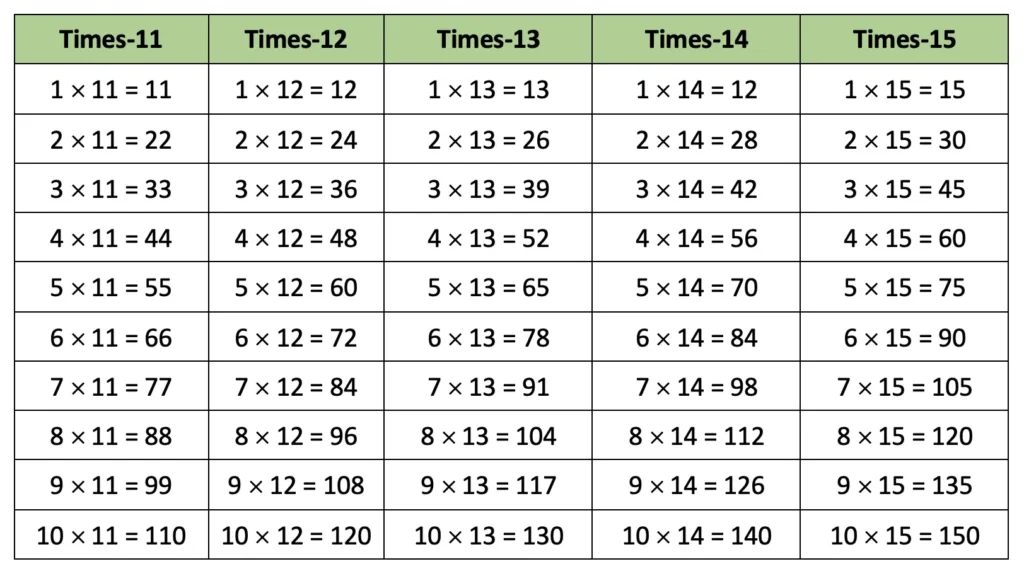
3. Construct other times-tables for numbers from 11 to 20, as you did for 15.
Solution:
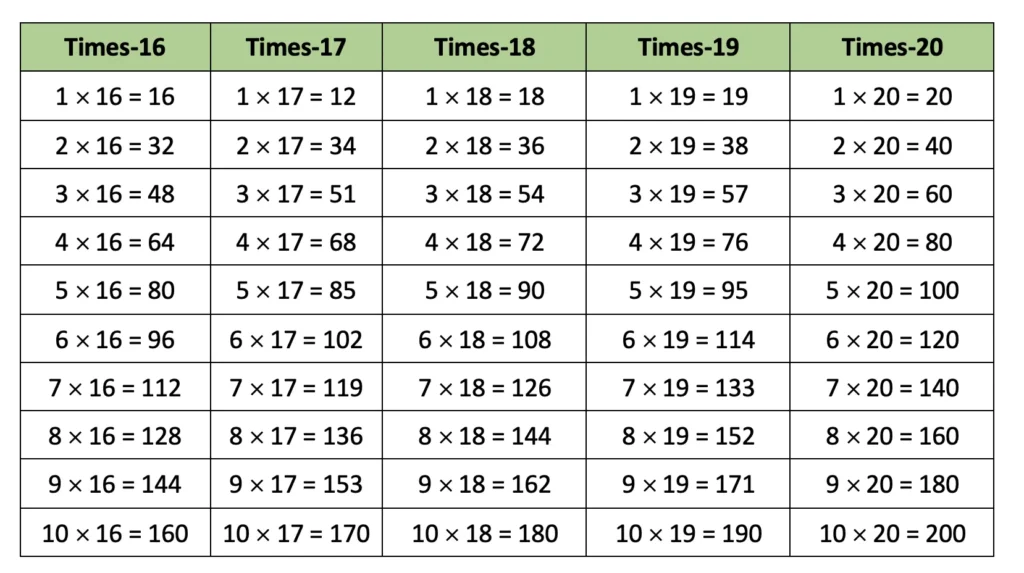
4. As you compared the times-5 table with the times-15 table, compare the times-1 table with the times-11 table, the times-2 table with the times-12 table, and so on. Share your observations.
Solution:
Do it yourself.
NCERT Textbook Page 187
Here is an arrangement of wheels. To count the total number of wheels, Tara splits them into two equal groups.
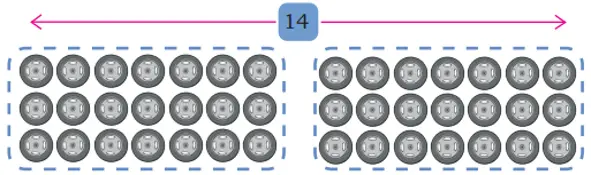
3 × 14 = 3 × 7 and 3 × 7
= 21 + 21 = double of 21
= 42.
Similarly, 6 × 14 can be obtained by splitting the arrangement into two equal groups.
6 × 14 = Double of 6 × 7 Why?
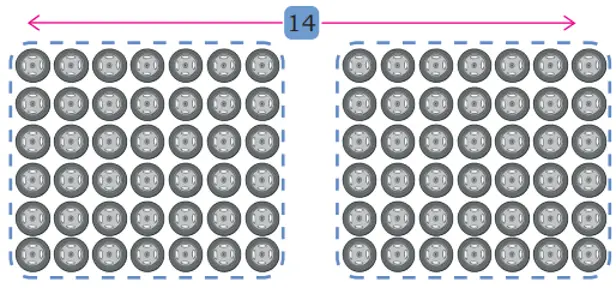
6 × 14 = 6 × 7 and 6 × 7
= 42 + 42 = double of 42
= 84.
NCERT Textbook Page 188
Q. We have seen how to calculate 3 × 14 and 6 × 14 by splitting and doubling. Can we construct the times-14 table by splitting and doubling? Try!
Solution:
Yes, times-14 can be constructed by spitting and doubling.
1 × 14 = 1 × 7 and 1 × 7
= 7 + 7 = double of 7 = 14.
2 ×14 = 2 × 7 and 2 × 7
= 14 + 14 = double of 14 = 28.
3 × 14 = 3 × 7 and 3 × 7
= 21 + 21 = double of 21 = 42.
4 × 14 = 4 × 7 and 4 × 7
= 28 + 28 = double of 28 = 56.
5 × 14 = 5 × 7 and 5 × 7
= 35 + 35 = double of 35 = 70.
6 × 14 = 6 × 7 and 6 × 7
= 42 + 42 = double of 42 = 84.
7 × 14 = 7 × 7 and 7 × 7
= 49 + 49 = double of 49 = 98.
8 × 14 = 8 × 7 and 8 × 7
= 56 + 56 = double of 56 = 112.
9 × 14 = 9 × 7 and 9 × 7
= 63 + 63 = double of 63 = 126.
10 × 14 = 10 × 7 and 10 × 7
= 70 + 70 = double of 70 = 140.
Q. What other times-tables can be constructed by splitting into equal groups and doubling? Give examples
Solution:
Times-tables for all even numbers like 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 etc. can be constructed by splitting into equal groups and doubling.
Examples:
4-times table = double of 2-times table.
6-times table = double of 3-times table.
Multiples of 10
Q. Find answers to the following:
a) 15 × 10 = _____ Tens = _____
b) 16 × 10 = _____ Tens = _____
c) 19 × 10 = _____ Tens = _____
d) 20 × 10 = _____ Tens = _____
Solution:
a) 15 × 10 = 15 Tens
= 10 Tens + 5 Tens = 100 + 50 = 150.
b) 16 × 10 = 16 Tens
= 10 Tens + 6 Tens = 100 + 60 = 160.
c) 19 × 10 = 19 Tens
= 10 Tens + 9 Tens = 100 + 90 = 190.
d) 20 × 10 = 20 Tens
= 10 Tens + 10 Tens = 100 + 100 = 200.
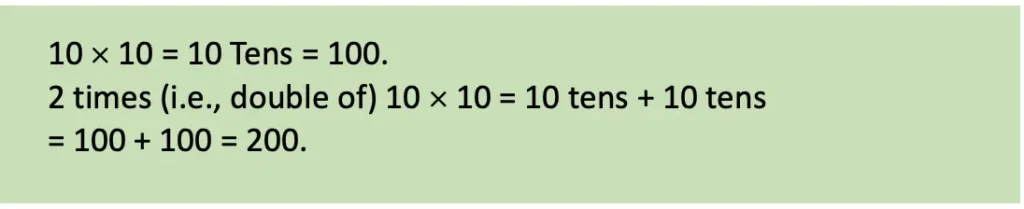
Textbook Page 189
Q. Now think and answer the following Problems.
30 × 10 = _____
40 × 10 = _____
50 × 10 = _____
60 × 10 = _____
70 × 10 = _____
80 × 10 = _____
Solution:
30 × 10 = 30 Tens = 300.
40 × 10 = 40 Tens = 400.
50 × 10 = 50 Tens = 500.
60 × 10 = 60 Tens = 600.
70 × 10 = 70 Tens = 700.
80 × 10 = 80 Tens = 800.
Q. Answer the following questions. Share your thoughts.
a) 21 × 10 = _____
b) 42 × 10 = _____
c) 65 × 10 = _____
d) 38 × 10 = _____
e) 53 × 10 = _____
f) 87 × 10 = _____
Solution:
a) 21 × 10 = 21 Tens
= 20 Tens + 1 tens = 200 + 10 = 210.
b) 42 × 10 = 42 Tens
= 40 Tens + 2 Tens = 400 + 20 = 420.
c) 65 × 10 = 65 Tens
= 60 Tens + 5 Tens = 600 + 50 = 650.
d) 38 × 10 = 38 Tens
= 30 Tens + 8 Tens = 300 + 80 = 380.
e) 53 × 10 = 53 Tens
= 50 Tens + 3 Tens = 500 + 30 = 530.
f) 87 × 10 = 87 Tens
= 80 Tens + 7 Tens = 800 + 70 = 870.
Textbook Page 190
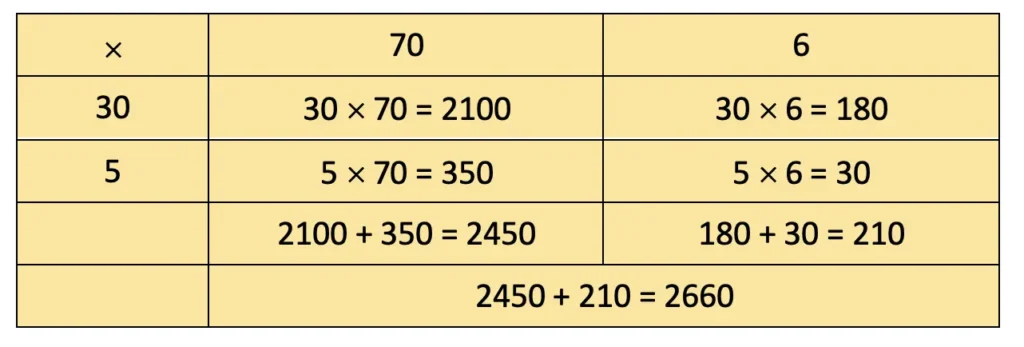
Q. Solve the following problems. Share your thoughts.
(i) 24 × 40 = _______
(ii) 50 × 60 = _______
(iii) 13 × 30 = _______
(iv) 43 × 60 = _______
(v) 70 × 80 = _______
Solution:
(i) 24 × 40 = 20 × 40 and 4 × 40
= 800 + 160 = 960.
(ii) 50 × 60 = 50 × 50 and 50 × 10
= 2500 + 500 = 3000.
(iii) 13 × 30 = 10 × 30 and 3 × 30
= 300 + 90 = 390.
(iv) 43 × 60 = 43 × 6 Tens
= 258 Tens = 2580.
(v) 70 × 80 = 70 × 8 Tens
= 560 Tens = 5600.
Textbook Page 192
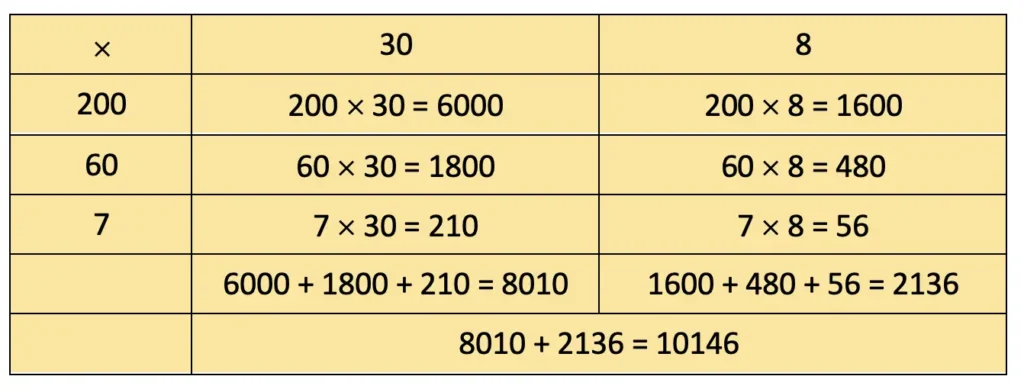
Q. Also, identify remainder (if any) in the division problems.
a) 25 × 34
b) 16 × 43
c) 68 × 12
d) 39 × 13
e) 125 ÷ 15
f) 94 ÷ 11
g) 440 ÷ 22
h) 508 ÷ 18
Solution:
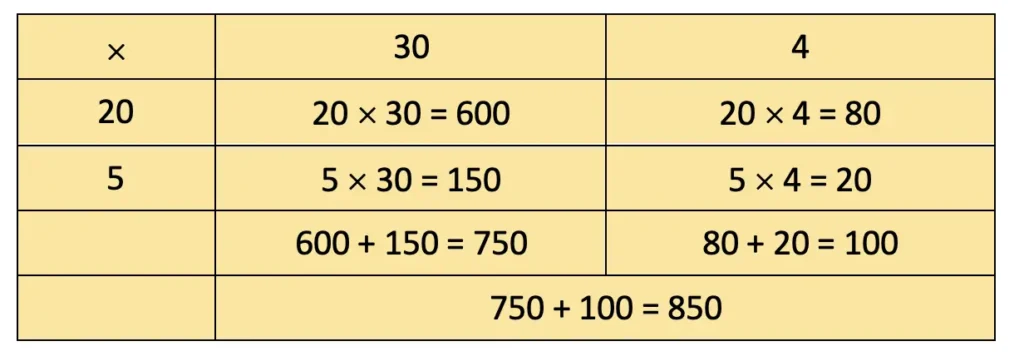
a) 25 × 34
= 600 + 80 + 150 + 20 = 850.
b) 16 × 43
= 400 + 30 + 240 + 18 = 688.

c) 68 × 12
= 600 + 120 + 80 + 16 = 816
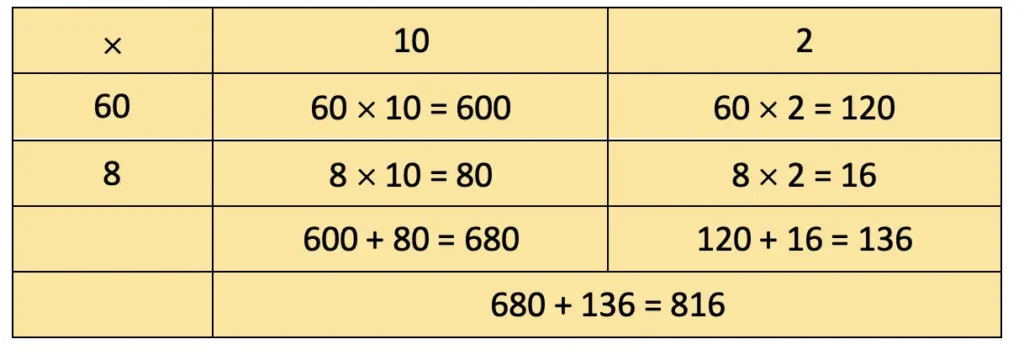
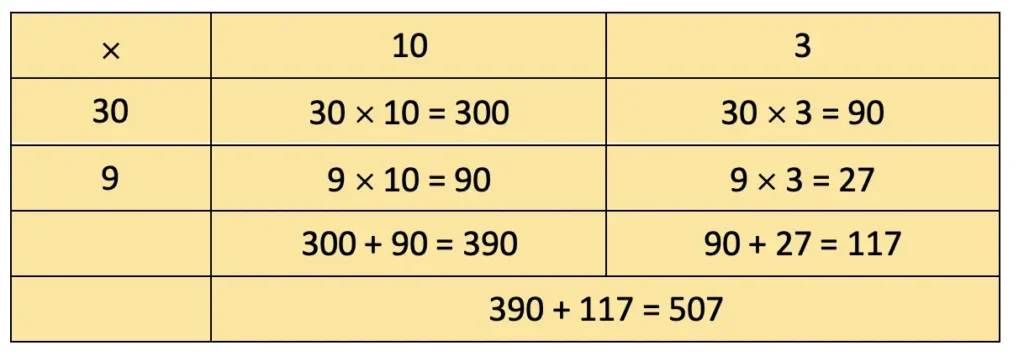
d) 39 × 13
= 300 + 90 + 90 + 27 = 507.
e) 125 ÷ 15
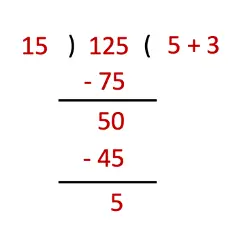
Thus, 125 ÷ 15 gives 8 (5 + 3) as quotient and 5 as remainder.
f) 94 ÷ 11
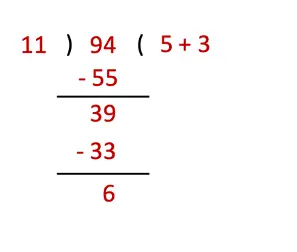
Thus, 94 ÷ 11 gives 8 (5 + 3) as quotient and 6 as remainder.
g) 440 ÷ 22

Thus, 440 ÷ 22 gives 20 (10 + 10) as quotient and 0 as remainder.
h) 508 ÷ 18

Thus, 508 ÷ 18 gives 28 (10 + 10 + 8) as quotient and 4 as remainder.
Multiples of 100
Q. 2 × 100 = 2 Hundreds = 200
3 × 100 = _____ Hundreds = ______
5 × 100 = _______ = __________
8 × 100 = ______ = _________
10 × 100 = 10 Hundreds = 1000
Solution:
2 × 100 = 2 Hundreds = 200
3 × 100 = 3 Hundreds = 300
5 × 100 = 5 Hundreds = 500
8 × 100 = 8 Hundreds = 800
10 × 100 = 10 Hundreds = 1000
Q. What happens when we put 10 hundreds together?

11 × 100 = 11 Hundreds
= 10 Hundreds + 1 Hundred
= 1000+ 100 = 1100
12 × 100 = _______
15 × 100 = _______
20 × 100 = 20 Hundreds = 2000
27 × 100 = _______
70 × 100 = _______
Solution:
12 × 100 = 12 Hundreds
= 10 Hundreds + 2 Hundreds
= 1000 + 200 = 1200
15 × 100 = 15 Hundreds
= 10 Hundreds + 5 Hundreds
= 1000 + 500 = 1500
27 × 100 = 27 Hundreds
= 20 Hundreds + 7 Hundreds
= 2000 + 700 = 2700
70 × 100 = 70 Hundreds = 7000
Textbook Page 193
Q. Now answer the following questions. Share your thoughts.
30 × 100 = ________
40 × 100 = ________
50 × 100 = ________
24 × 100 = ________
53 × 100 = ________
19 × 100 = ________
We know
80 × 100 = 8000
80 × 50 = ________
40 × 50 = ________
Solution:
30 × 100 = 20 × 100 and 10 × 100
= 2000 + 1000 = 3000
40 × 100 = 20 × 100 and 20 × 100
= 2000 + 2000 = 4000
50 × 100 = 30 × 100 and 20 × 100
= 3000 + 2000 = 5000
24 × 100 = 20 × 100 and 4 × 100
= 2000 + 400 = 2400
53 × 100 = 50 × 100 and 3 × 100
= 5000 + 300 = 5300
19 × 100 = 10 × 100 and 9 × 100
= 1000 + 900 = 1900
80 × 50 = 4000
40 × 50 = 2000
Textbook Page 194
Q. Share what you notice about the answers to these problems.
11 × 100 = _______
11 × 200 = _______
22 × 100 = _______
22 × 200 = _______
Solution:
11 × 100 = 10 × 100 and 1 × 100
= 1000 + 100 = 1100
11 × 200 = 11 × 100 and 11 × 100
= 1100 + 1100 = 2200
22 × 100 = 11 × 100 and 11 × 100
= 1100 + 1100 = 2200
22 × 200 = 22 × 100 and 22 × 100
= 2200 + 2200 = 4400
Q. Answer the following questions. Share your thoughts.
18 × 100 = _______
5 × 500 = _______
15 × 200 = _______
14 × 300 = _______
23 × 200 = _______
7 × 800 = _______
Solution:
18 × 100 = 10 × 100 and 8 × 100
= 1000 + 800 = 1800
5 × 500 = 5 × 5 Hundreds
= 25 Hundreds = 25 × 100 = 2500
15 × 200 = 15 × 100 and 15 × 100
= 1500 + 1500 = 3000
23 × 200 = 23 × 100 and 23 × 100
= 2300 + 2300 = 4600
7 × 800 = 7 × 8 Hundreds
= 56 Hundreds
Textbook Page 195
Q. Find the answers in Set A. Examine the relationships between the problems and the answers in Set A carefully. Then use this understanding to find the answers in Set B.
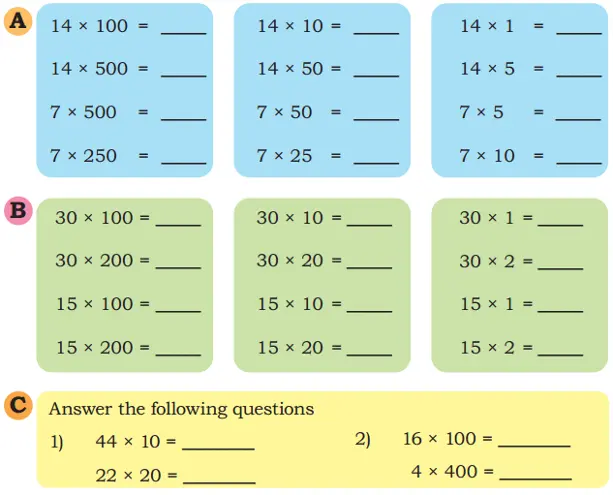
Solution:
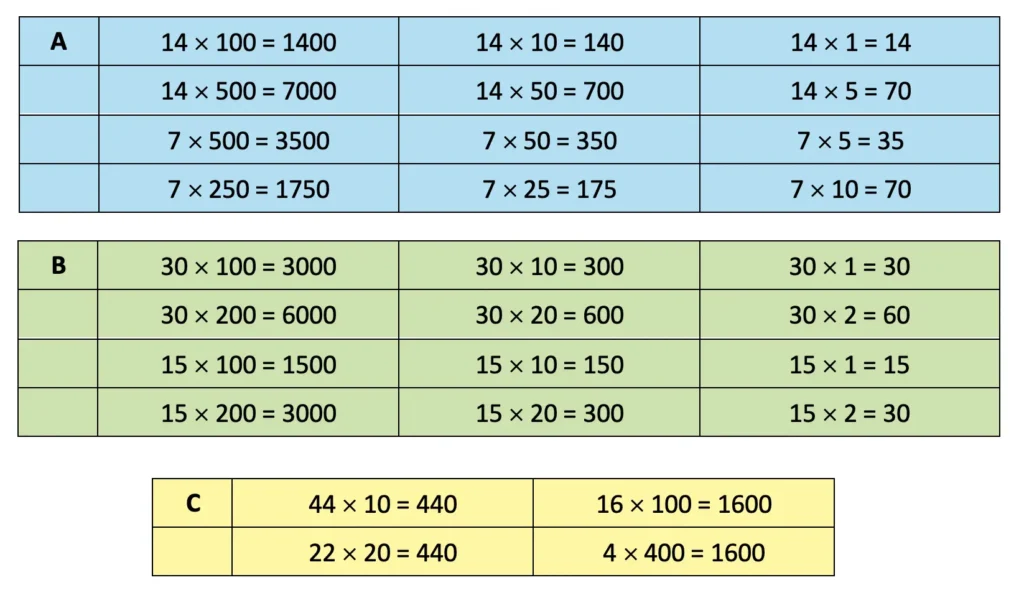
Textbook Page 197
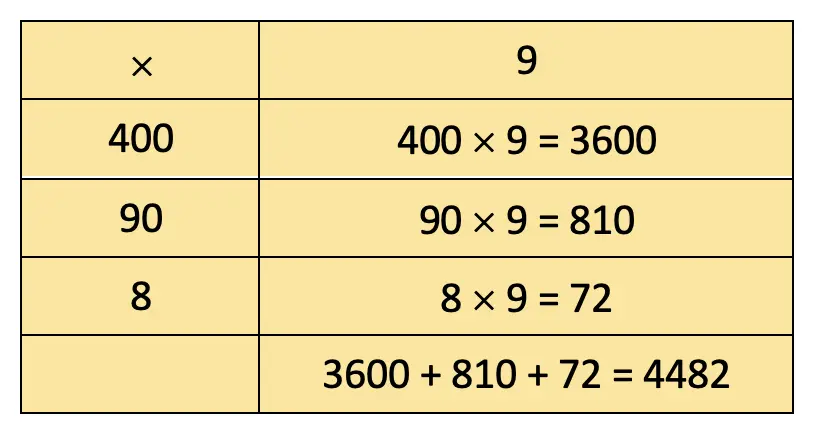
Q. Also, identify remainder (if any) in the division problems.
a) 237 × 28
b) 140 × 16
c) 389 × 57
d) 807 ÷ 24
e) 692 ÷ 33
f) 996 ÷ 45
Solution:
a) 237 × 28
= 4000 + 1600 + 600 + 240 + 140 + 56 = 6636.
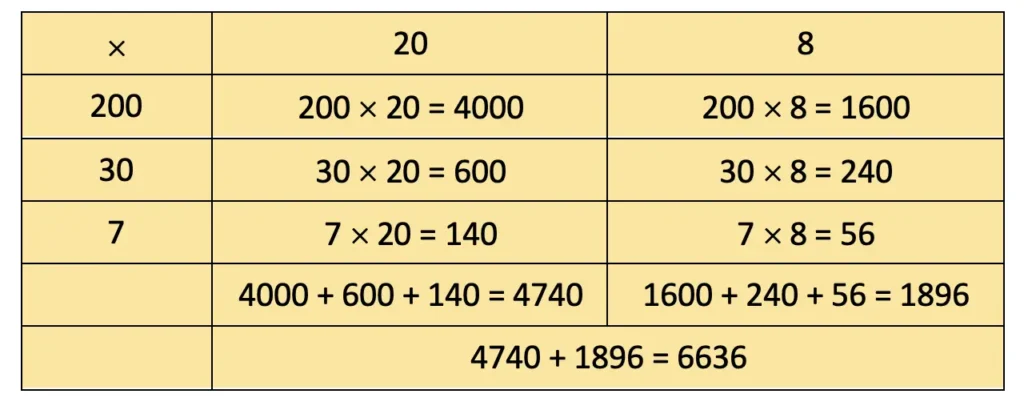
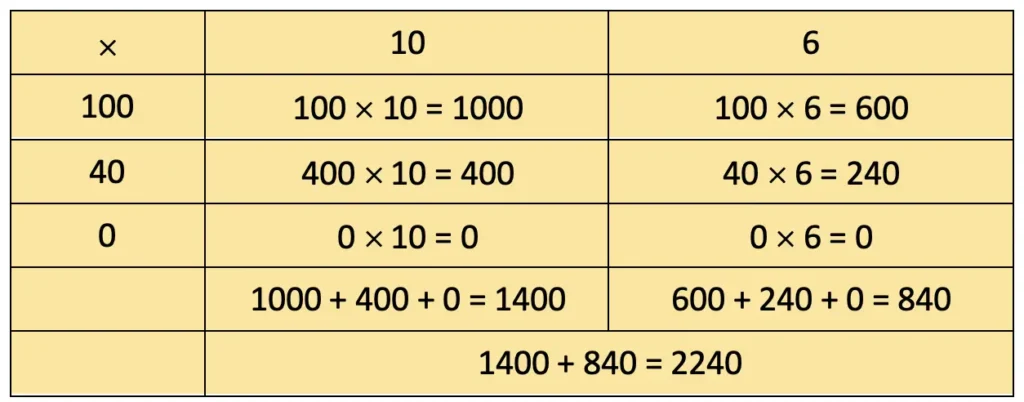
b) 140 × 16
= 1000 + 600 + 400 + 240 = 2240.
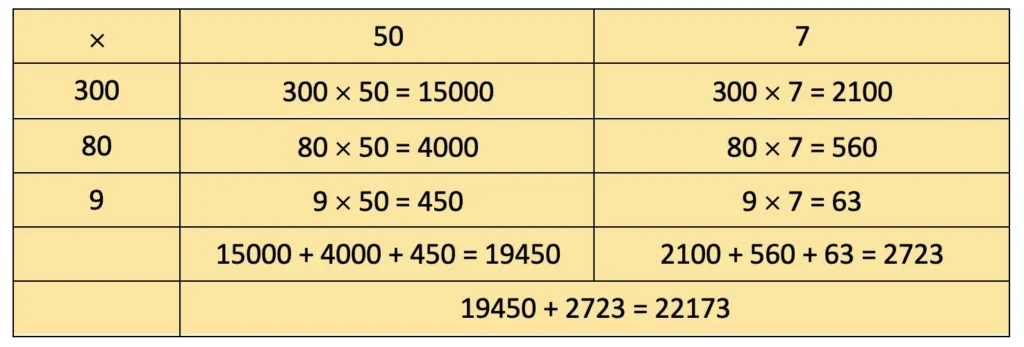
c) 389 × 57
= 15000 + 2100 + 14000 + 560 + 450 + 63 = 22173.
d) 807 ÷ 24

807 ÷ 24 gives 33 (10 + 10 + 10 + 3) as quotient and 15 as remainder.
e) 692 ÷ 33

692 ÷ 33 gives 20 (10 + 10) as quotient and 32 as remainder.
f) 996 ÷ 45

996 ÷ 45 gives 22 (10 + 10 + 2) as quotient and 6 as remainder.
Dividing by 10 and 100
Q. A farmer packs his rice in sacks of 10 kg each.
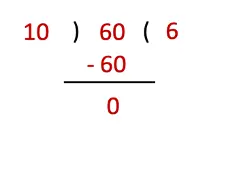
(а) If he has 60 kg of rice, how many sacks does he need?
Solution:
Rice in one sac = 10 kg
Total quantity of rice = 60 kg
No. of sacs needed = 60 ÷ 10 = 6.
b) If he has 600 kg of rice, how many sacks does he need?
Solution:
Rice in one sac = 10 kg
Total quantity of rice = 600 kg
No. of sacs needed = 600 ÷ 10 = 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 = 60.

Q. 60 ÷ 10 = _______
600 ÷ 10 = _______
600 ÷ 100 = _______
Solution:
60 ÷ 10 = 6
600 ÷ 10 = 60
600 ÷ 100 = 6
Textbook Page 198
Q. Find the answers to the following questions. Share your thoughts in class.
40 ÷ 10 = ____
400 ÷ 10 = ____
400 ÷ 100 = ____
4 ÷ 2 = ____
40 ÷ 20 = ____
400 ÷ 200 = ____
400 ÷ 2 = ____
400 ÷ 20 = ____
400 ÷ 200 = ____
Solution:
40 ÷ 10 = 4
4 ÷ 2 = 2
400 ÷ 2 = 200
400 ÷ 10 = 40
40 ÷ 20 = 2
400 ÷ 20 = 20
400 ÷ 100 = 4
400 ÷ 200 = 2
400 ÷ 200 = 2
Q. Think and answer. Write the division statement in each case.
1. Manku the monkey sees 870 bananas in the market. Each bunch has 10 bananas. How
many bunches are there in the market? _______
Solution:
Total Bananas = 870
No. of bananas in a bunch = 10
No. of bunches of bananas = 870 ÷ 10 = 87.
Division statement: 870 ÷ 10 = 87.
2. Rukhma Bi wants to distribute ₹1000/- equally among her 10 grandchildren on the occasion of Eid. How much money will each of them get? ________
Solution:
Money to distribute = ₹1000
No. of grandchildren = 10
Money each grandchild will get = ₹1000 ÷ 10 = 100.
Division statement: ₹1000 ÷ 10 = ₹100.
Let Us Solve
1. The oldest long-distance train of the Indian Railways is the Punjab Mail which ran between Mumbai and Peshawar. Its first journey was on 12 October 1912. Do you I know how many coaches it had on its first journey? It had 6 coaches: 3 carrying 96 passengers and 3 for goods.
a) How many people travelled in each coach on the first journey?
b) This train has been running for 106 years now. It runs between Mumbai, Maharashtra and Ferozepur, Punjab. It has 24 coaches. Each coach can carry 72 passengers. How many people can travel on this train?
Solution:
a) No. of coaches carrying passengers on the first journey = 3
Total passengers travelled = 96
People travelled in each coach on the first journey = 96 ÷ 3 = 10 + 10 + 10 + 2 = 32.

b) No. of coaches in train now = 24
No. of passengers each coach carries now = 72
People travelling on train = 24 × 72 = 1680 + 48 = 1728.

Textbook Page 199
2. Amala and her 35 classmates, along with 6 teachers, are going on a school trip to Goa. They are using the double-decker “hop on hop off” sightseeing bus to explore the city.
a) 2 people can sit on every seat of the bus. There are 15 seats in the lower deck and 10 in the upper deck. How many seats will they need to occupy? Are there enough seats for everyone?
b) Find the total cost of the tickets for all children.
c) What is the cost of the tickets for all teachers?

Solution:
a) Total people on bus = 1 + 35 + 6 = 42
No. of people that can sit on a seat = 2
Seats people will occupy = 42 ÷ 2 = 21.

Total seats in the bus = 15 + 10 = 25 seats
Yes, there are enough seats in the bus for everyone because the total seats are more than the seats that will get occupied.
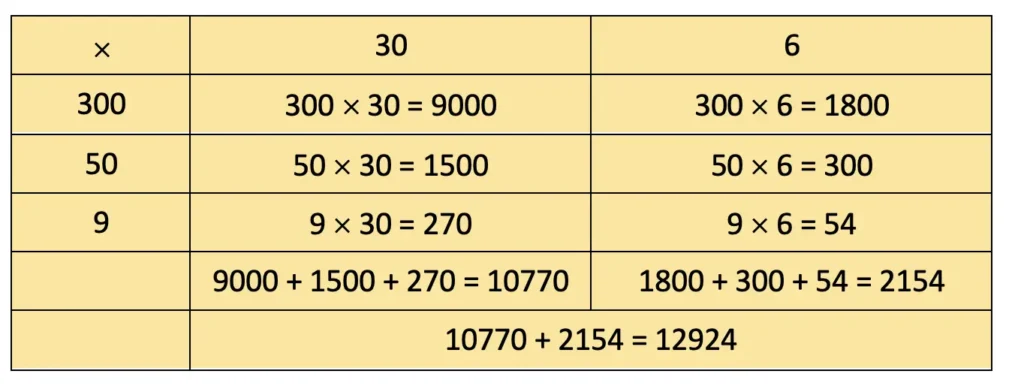
b) Total children on bus = 36
Cost of ticket for each child = ₹359
Cost of tickets for all children = ₹359 × 36 = ₹12924.
c) Total teachers on bus = 6
Cost of ticket for each teacher = ₹899
Cost of ticket for all teachers = ₹899 × 6 = ₹5394
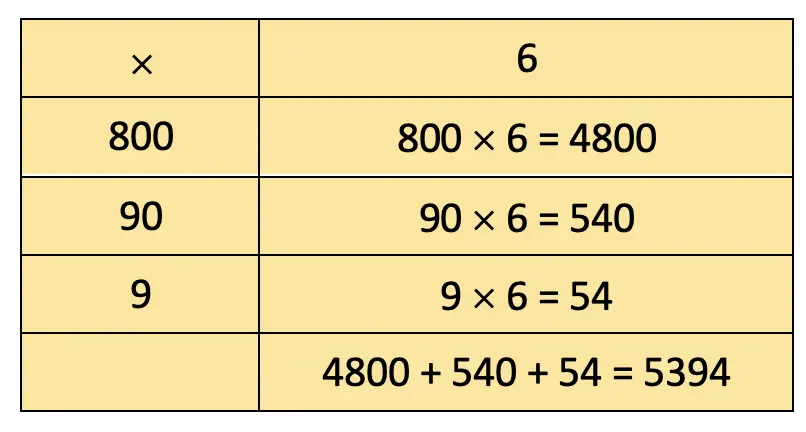
3. Kedar works in a brick kiln.
a) The kiln makes 125 bricks in a day. How many bricks can be made in a month?
b) Each brick is sold in the market for ₹ 9. How much money can they earn in a month?
Solution:
a) Bricks made in a day = 125
Total bricks made in a month = 30 × 125 = 3750.
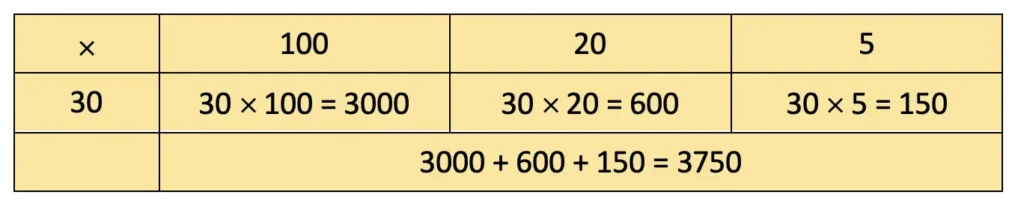
b) Price of a brick = ₹ 9
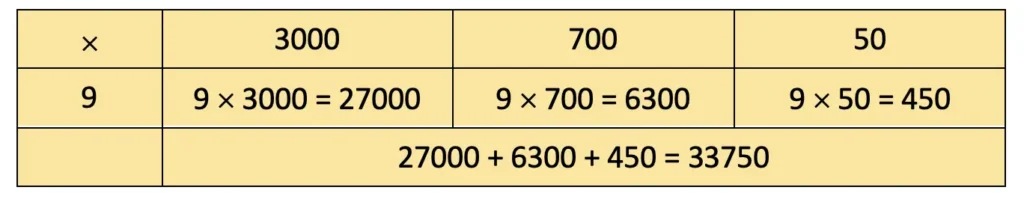
Total bricks made in a month = 3750
Total money earned in a month = ₹ 9 × 3750 = ₹33750.
4. Chilika lake in Odisha is the largest saltwater lake in India. It is famous for the Irrawaddy dolphins. Boats can be hired to go see the dolphins. The trip from Puri includes a bus ride followed by a boat ride. Eight people will be going on the trip.

• A bus ticket from Puri to Satapada costs ₹ 60.
• A two-hour boat ride for 8 people costs ₹ 1200.
• How much money do we need to spend on each person?
Solution:
No. of people going on the trip = 8
Cost of bus ticket for a person = ₹ 60
Cost of boat ride for 8 people = ₹ 1200
Cost of boat ride for a person = ₹ 1200 ÷ 8 = ₹ 150.

Total money required to spend on each person = ₹ 60 + ₹ 150 = ₹ 210.
Textbook Page 200
5. Find the multiplication and division sentences below. Shade the sentences. How many can you find? Some are done for you.
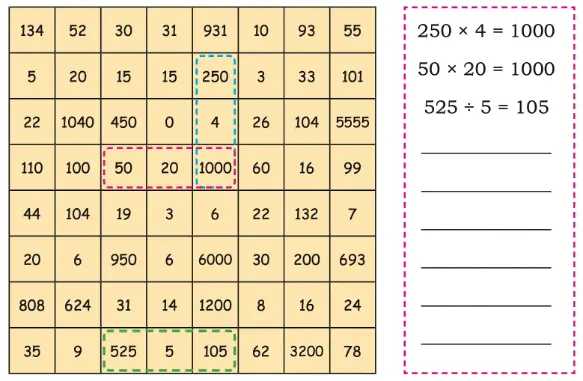
Solution:
6. Solve:
a) 35 × 76
Solution:
b) 267 × 38
Solution:
c) 498 × 9
Solution:
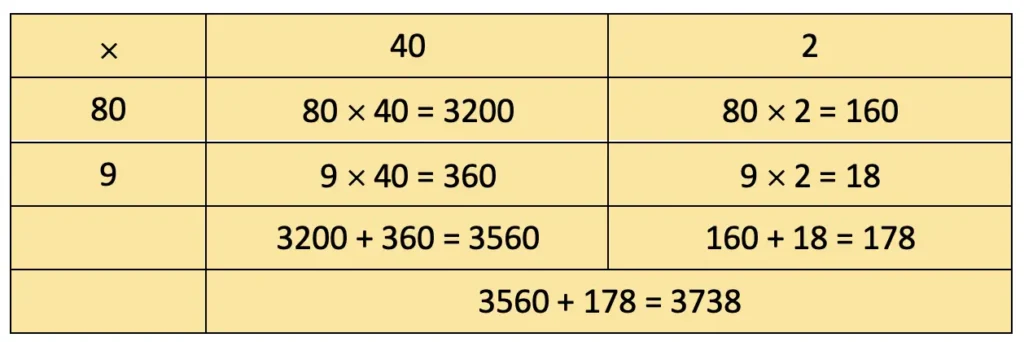
d) 89 × 42
Solution:
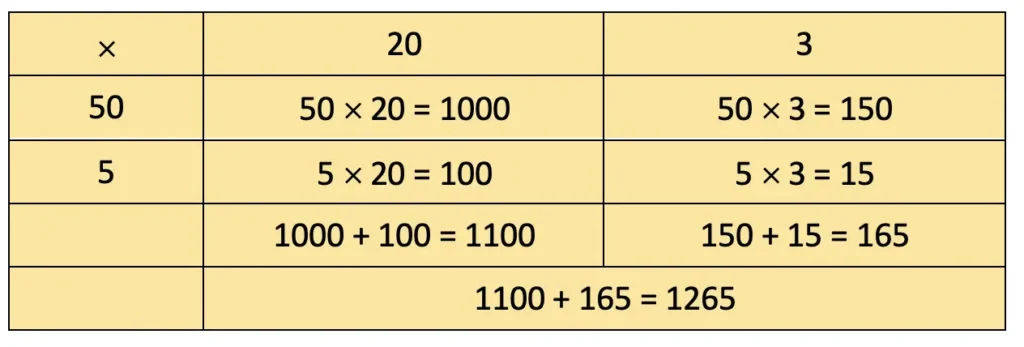
e) 55 × 23
Solution:
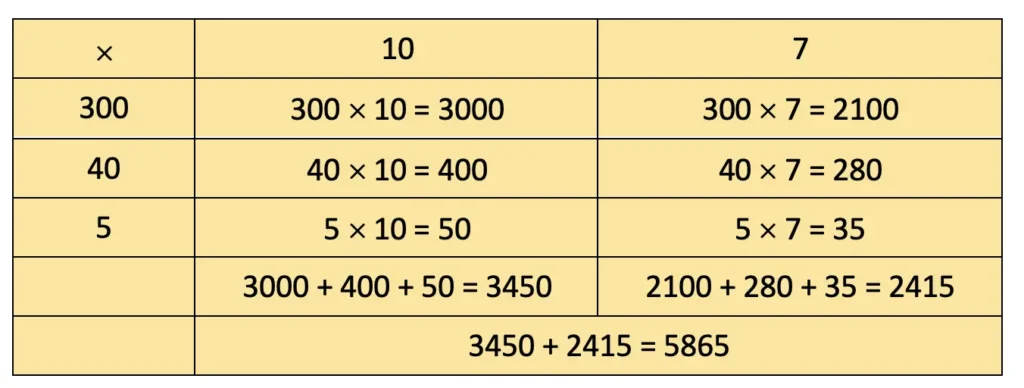
f) 345 × 17
Solution:
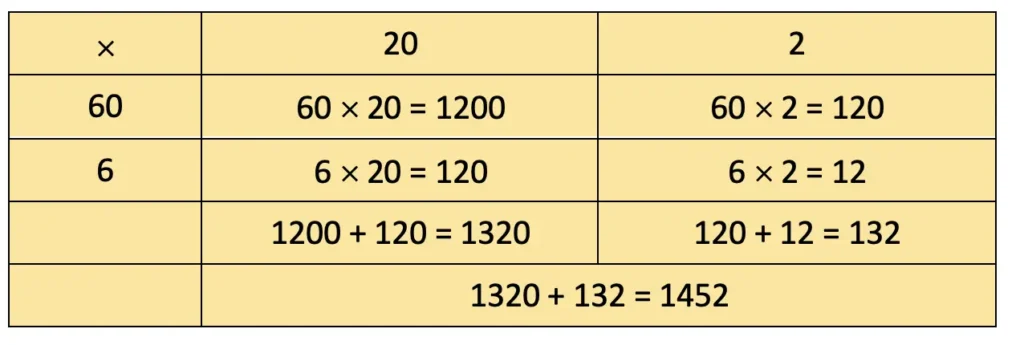
g) 66 × 22
Solution:
h) 704 × 11
Solution:
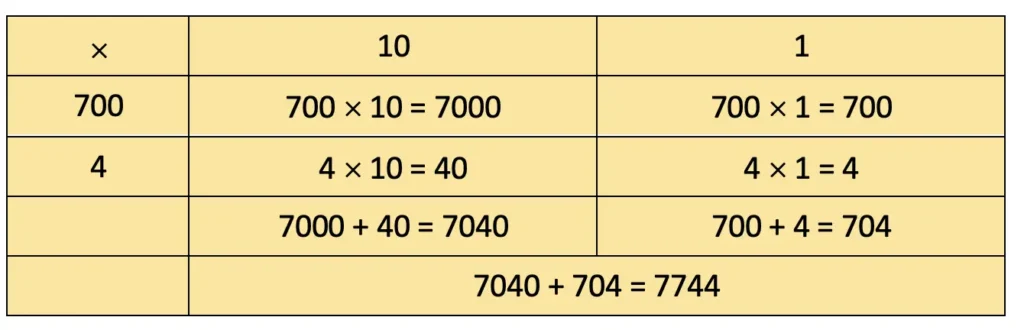
i) 319 × 26
Solution:
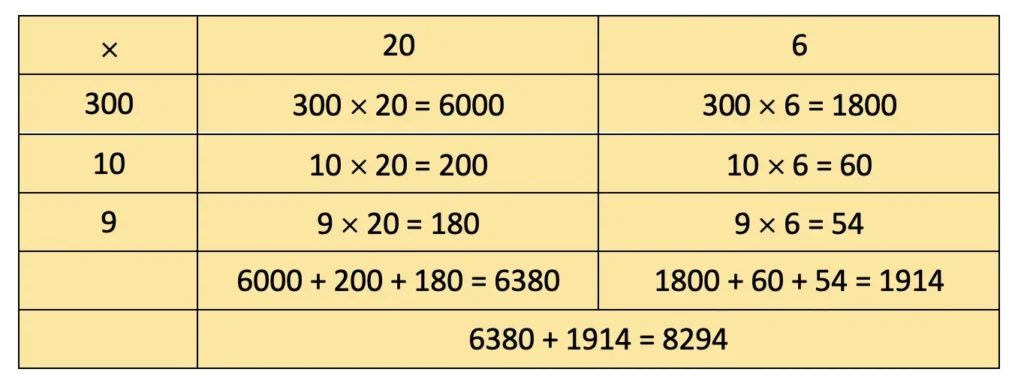
j) 459 ÷ 3
Solution:

Therefore, 459 ÷ 3 gives a quotient of 153 (100 + 50 + 3) and a remainder of 0.
k) 774 ÷ 18
Solution:

Therefore, 774 ÷ 18 gives a quotient of 43 (10 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 3) and a remainder of 0.
l) 864 ÷ 26
Solution:

Therefore, 864 ÷ 26 gives a quotient of 23 (10 + 10 + 10 + 3) and a remainder of 6.
m) 304 ÷ 12
Solution:

Therefore, 304 ÷ 12 gives a quotient of 25 (10 + 10 + 5) and a remainder of 4.
n) 670 ÷ 9
Solution:

Therefore, 670 ÷ 9 gives a quotient of 74 (50 + 20 + 4) and a remainder of 4.
o) 584 ÷ 25
Solution:

Therefore, 584 ÷ 25 gives a quotient of 23 (10 + 10 + 3) and a remainder of 9.
p) 900 ÷ 15
Solution:

Therefore, 900 ÷ 15 gives a quotient of 60 (50 + 10) and a remainder of zero.
q) 658 ÷ 32
Solution:

Therefore, 658 ÷ 32 gives a quotient of 20 (10 + 10) and a remainder of 18.
r) 974 ÷ 9
Solution:

Therefore, 974 ÷ 9 gives a quotient of 108 (50 + 50 + 8) and a remainder of 2.
Textbook Page 201
Chinnu’s Coin
1. Five friends plan to visit an amusement park nearby. Each of them uses different notes and coins to buy the ticket. The cost of the ticket is ₹ 750.

• Bujji has brought all notes of ₹ 200.
• And Munna has brought all notes of ₹ 50.
• Whereas Balu has brought all notes of ₹ 20.
• And guess what, Chinnu has all coins of ₹ 5.
• And Sansu has all coins of ₹ 2.
(a) Find out how many notes/coins each child has to bring to buy the ticket.
(b) Which of these children will not receive any change from the cashier?
(c) How long would the cashier take to count Chinnu’s coins?
Solution:
(a)
(i) No. of notes Bujji needs to buy the ticket = 750 ÷ 200
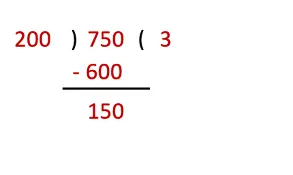
So, Bujji has to bring 4 notes of ₹200 to buy the ticket.
(ii) No. of notes Munna needs to buy the ticket = 750 ÷ 50

So, Munna has to bring 15 notes of ₹ 50 to buy the ticket.
(iii) No. of notes Balu needs to buy the ticket = 750 ÷ 20

So, Balu has to bring 37 + 1 = 38 notes of ₹ 20 to buy the ticket.
(iv) No. of coins Chinnu needs to buy the ticket = 750 ÷ 5

So, Chinnu needs to bring 150 coins of ₹ 5 to buy the ticket.
(v) No. of coins Sansu needs to buy the ticket = 750 ÷ 2

So, Sansu needs to bring 375 coins of ₹ 2 to buy the ticket.
(b) Munna, Chinnu and Sansu will not receive any change from the cashier.
(c) 750 ÷ 5 = 150.

So, the cashier would count 150 times to count Chinnu’s coins.
2. Observe the following multiplications. The answers have been provided.
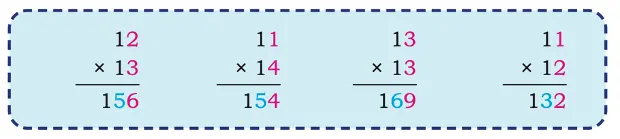
In each case, do you see any pattern in the two numbers and their product? (Hint: Look at the coloured digits!)
For what other multiplication problems will this pattern hold? Find 5 such examples.
Solution:
Patterns observed:
Units digit of the product = product of the units digits of the two numbers.
Tens digit of the product = sum of the units digits of the two numbers.
Some other examples:
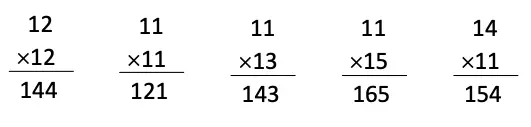
Textbook Page 202
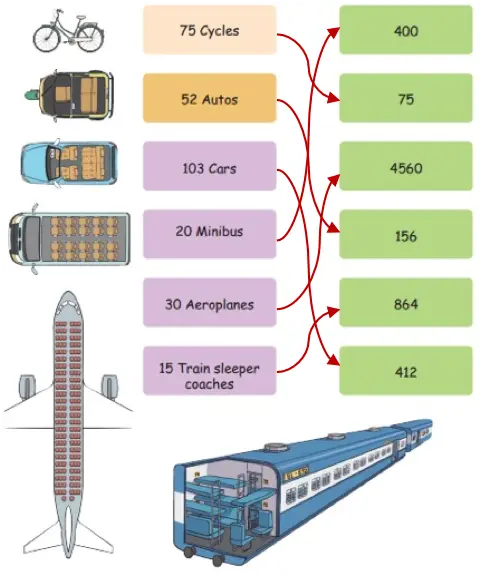
3. Assume each vehicle is travelling with full capacity. How many people can travel in each of these vehicles? Match them up.
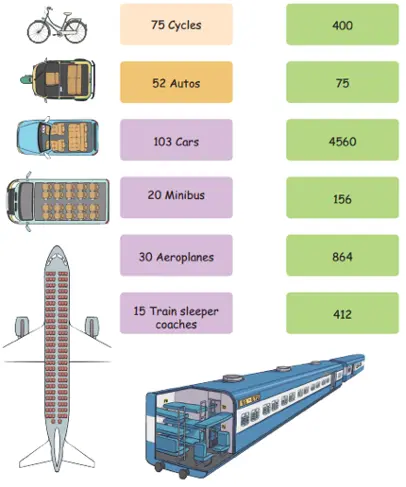
Solution: