Class 8 Science Curiosity Chapter 2 The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye NCERT Solutions
Textbook Page 25 – 26
Keep the curiosity alive
1. Various parts of a cell are given below. Write them in the appropriate places in the following diagram.
Nucleus, Chloroplast, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Cell wall, Nucleoid.
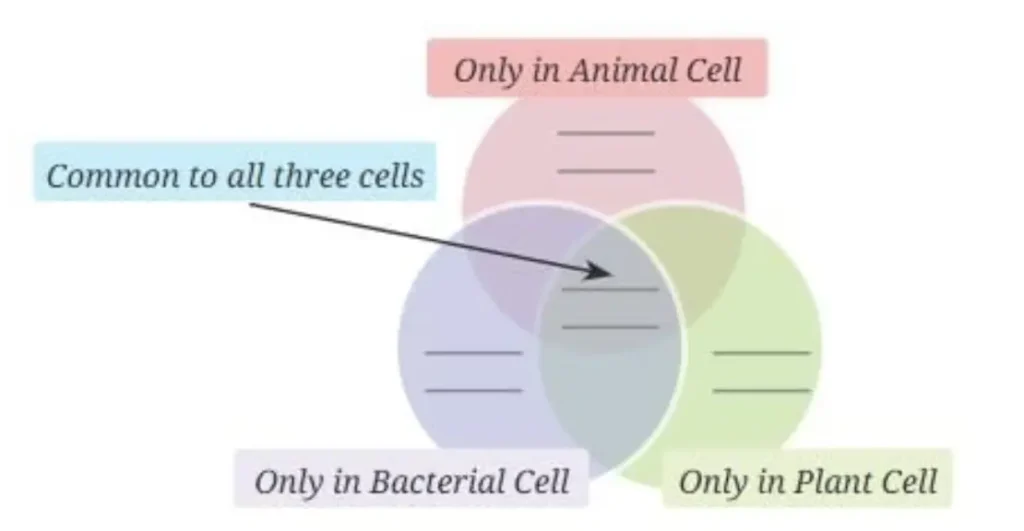
Answer:
Common to all three cells: Nucleus and Cytoplasm.
Only in Animal Cell: None of the given parts are exclusive to the animal cell.
Only in Bacterial Cell: Nucleoid and Cell Wall.
Only in Plant Cell: Chloroplast and Cell Wall.
2. Aanandi took two test tubes and marked them A and B. She put two spoonfuls of sugar solution in each of the test tubes. In test tube B, she added a spoonful of yeast. Then she attached two incompletely inflated balloons to the mouth of each test tube. She kept the setup in a warm place, away from sunlight.
(i) What do you predict will happen after 3–4 days? She observed that the balloon attached to testtube B was inflated. What can be a possible explanation for this?
(a) Water evaporated in test tube B and filled the balloon with the water vapour.
(b) The warm atmosphere expanded the air inside the test tube B, which inflated the balloon.
(c) Yeast produced a gas inside the test tube B which inflated the balloon.
(d) Sugar reacted with warm air, which produced gas, eventually inflating the balloon.
(ii) She took another test tube, 1/4 filled with lime water. She removed the balloon from test tube B in such a manner that the gas inside the balloon did not escape. She attached the balloon to the test tube with lime water and shook it well. What do you think she wants to find out?

Answer:
(i)
(c) Yeast produced a gas inside the test tube B, which inflated the balloon.
(ii) Aanandi wants to find out whether the gas collected in the balloon from test tube B is carbon dioxide. To test this, she shakes the gas with lime water. If the lime water turns milky, it confirms the presence of carbon dioxide. This is because carbon dioxide reacts with lime water to form calcium carbonate, which appears as a milky white precipitate.
3. A farmer was planting wheat crops in his field. He added nitrogen-rich fertiliser to the soil to get a good yield of crops. In the neighbouring field, another farmer was growing bean crops, but she preferred not to add nitrogen fertiliser to get healthy crops. Can you think of the reasons?
Answer:
Roots of certain leguminous plants like beans, peas, and lentils have root nodules that contain Rhizobium bacteria. These bacteria capture nitrogen from the air and convert it into a form that plants can use. This natural process of nitrogen fixation provides the plants with the necessary nutrients, making it unnecessary for the farmer to add nitrogen-rich fertilisers. That is why the second farmer, who was growing bean crops, chose not to use nitrogen fertiliser.
4. Snehal dug two pits, A and B, in her garden. In pit A, she put fruit and vegetable peels and mixed it with dried leaves. In pit B, she dumped the same kind of waste without mixing it with dried leaves. She covered both the pits with soil and observed after 3 weeks. What is she trying to test?
Answer:
Snehal is trying to test whether adding dried leaves to fruit and vegetable peels helps micro-organisms decompose the waste more effectively into nutrient-rich manure. By mixing dried leaves in pit A and not in pit B, she wants to observe if the decomposition process is faster or more efficient when dried leaves are added.
5. Identify the following microorganisms:
(i) I live in every kind of environment, and inside your gut.
(ii) I make bread and cakes soft and fluffy.
(iii) I live in the roots of pulse crops and provide nutrients for their growth.
Answer:
(i) Bacteria – They are found in all kinds of environments, including water, soil, air, and even inside our gut, where they help in digesting food.
(ii) Yeast – It is a type of fungus that makes bread and cakes soft and fluffy by converting the sugar in the dough into carbon dioxide and alcohol through the process of fermentation.
(iii) Rhizobium bacteria – These bacteria live in the root nodules of leguminous plants. They fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into a form that plants can use, thus enriching the soil with nutrients.
6. Devise an experiment to test that microorganisms need optimal temperature, air, and moisture for their growth.
Answer:
Materials Needed: Two bowls, flour (atta or maida), warm water, yeast, sugar, and a damp cloth.
Procedure:
(i) Take two bowls and label them as A and B.
(ii) In each bowl, add 200 g of flour and a pinch of sugar.
(iii) Add a small amount of yeast to both bowls and mix it well with the flour.
(iv) Knead the flour in both bowls using warm water to make a soft dough.
(v) Cover the dough in bowl A with a damp cloth and keep it in a warm place.
(vi) Cover the dough in bowl B and place it in a refrigerator.
Expected Results:
(i) The dough in bowl A will become porous and fluffy. This is because microorganisms like yeast grow and multiply best in warm, moist conditions with proper air supply.
(ii) The dough in bowl B will show little or no fluffiness due to the slowdown of microbial activity at low temperatures.
Conclusion: Microorganisms need optimal temperature, air, and moisture for their growth.
7. Take 2 slices of bread. Place one slice in a plate near the sink. Place the other slice in the refrigerator. Compare after three days. Note your observations. Give reasons for your observations.
Answer:
Observations:
(i) The bread slice kept near the sink shows signs of mold after three days.
(ii) The bread slice placed in the refrigerator shows little or no mold growth.
Reasons:
(i) The area near the sink is warm and humid, which creates ideal conditions for microorganisms to grow.
(ii) The refrigerator has a cool temperature, which slows down the activity and reproduction of microorganisms, preventing or delaying the growth of mold.
8. A student observes that when curd is left out for a day, it becomes more sour. What can be two possible explanations for this observation?
Answer:
(i) Curd contains Lactobacillus bacteria, which convert the sugar in milk (lactose) into lactic acid. This acid gives curd its sour taste. When curd is left out for a day, especially in warm conditions, the bacteria multiply rapidly and produce more lactic acid, making the curd more sour.
(ii) Higher temperatures accelerate the fermentation process, allowing bacteria to act faster. This leads to increased production of lactic acid in a shorter time, resulting in greater sourness.
9. Observe the set-up given in Fig. 2.15 and answer the following questions.
(i) What happens to the sugar solution in flask A?
(ii) What do you observe in test tube B after four hours? Why do you think this happened?
(iii) What would happen if yeast was not added in flask A?
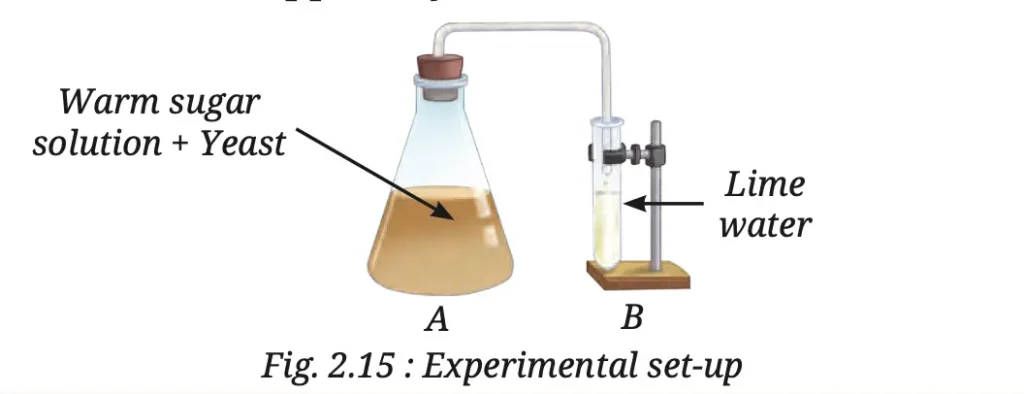
Answer:
(i) In flask A, yeast ferments the sugar solution by breaking down the sugar into carbon dioxide and alcohol through the process of fermentation.
(ii) After four hours, the lime water in test tube B turns milky. This occurs because the carbon dioxide gas produced during fermentation in flask A passes through the delivery tube and reacts with the lime water, forming a white precipitate of calcium carbonate.
(iii) If yeast were not added to flask A, fermentation would not occur. As a result, no carbon dioxide would be produced, and the lime water in test tube B would remain clear (not turn milky).
