Class 8 Science Curiosity Chapter 4 Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects NCERT Solutions
Probe and ponder (Page 46)
Q. If we don’t have an electric lamp while making an electric circuit with an electric cell, is there any other way through which we can find out if current is flowing in the circuit?
Answer:
We can find out if current is flowing in the circuit:
(i) By placing a magnetic compass needle near the circuit — it will show deflection when current flows.
(ii) By connecting an ammeter or galvanometer in the circuit.
(iii) By using a small buzzer, which will produce sound when current flows.
(iv) By observing heating of the circuit components — if current flows, the wire or device becomes warm.
Q. Is it possible to make temporary magnets? How can these be made?
Answer:
Yes, it is possible to make temporary magnets. They can be made by passing current through a coil of wire wound around an iron core. The coil behaves like a magnet as long as the current flows through it. When the current is switched off, it loses its magnetism.
Q. We can generate heat by burning fossil fuels and wood; but how is heat generated in various electrical appliances?
Answer:
Heat in electrical appliances is produced due to the heating effect of electric current. These appliances have a coil of wire called the heating element. When electric current passes through the element, it becomes hot and produces heat.
Q. How do we know if a cell or a battery is dead? Can all cells and batteries be recharged?
Answer:
We know that a cell or battery is dead when it does not light a bulb or run an electrical device.
No, all cells and batteries can be recharged. A dry cell is for single use and has to be disposed of after use, while rechargeable batteries can be recharged and used many times.
Keep the curiosity alive (Page 58 – 61)
1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) The solution used in a Voltaic cell is called ________.
(ii) A current carrying coil behaves like a _______ .
Answer:
(i) electrolyte.
(ii) magnet.
2. Choose the correct option:
(i) Dry cells are less portable compared to Voltaic cells. (True/False)
(ii) A coil becomes an electromagnet only when electric current flows through it. (True/False)
(iii) An electromagnet, using a single cell, attracts more iron paper clips than the same electromagnet with a battery of 2 cells. (True/False)
Answer:
(i) False.
Dry cells are more portable than Voltaic cells because they don’t contain liquid electrolyte.
(ii) True.
(iii) False.
When more cells are connected, a higher current flows through the coil. This makes the electromagnet stronger, so it should attract more iron paper clips with 2 cells than with a single cell.
3. An electric current flows through a nichrome wire for a short time.
(i) The wire becomes warm.
(ii) A magnetic compass placed below the wire is deflected.
Choose the correct option:
(a) Only (i) is correct
(b) Only (ii) is correct
(c) Both (i) and (ii) are correct
(d) Both (i) and (ii) are not correct
Answer:
(c) Both (i) and (ii) are correct.
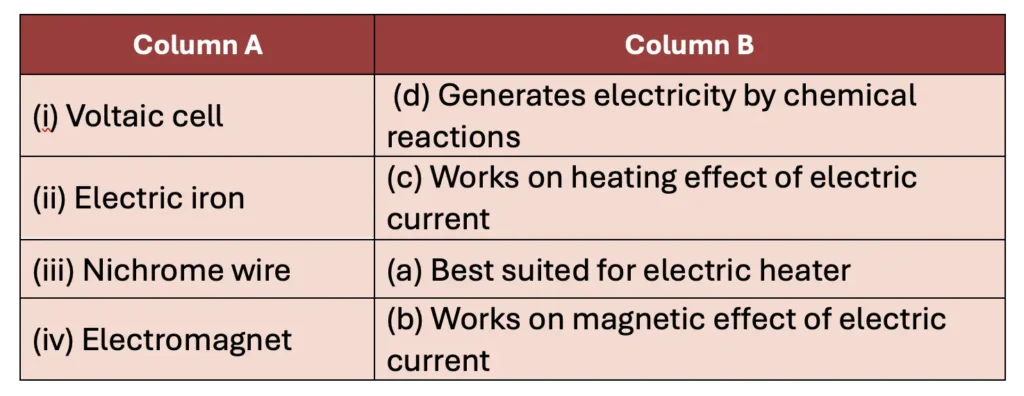
4. Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.
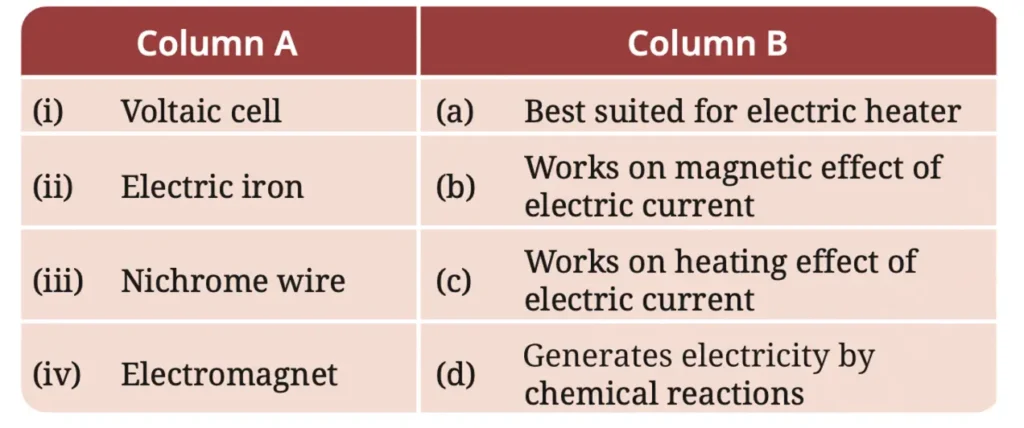
Answer:
5. Nichrome wire is commonly used in electrical heating devices because it
(i) is a good conductor of electricity.
(ii) generates more heat for a given current.
(iii) is cheaper than copper.
(iv) is an insulator of electricity.
Answer:
(ii) generates more heat for a given current.
6. Electric heating devices (like an electric heater or a stove) are often considered more convenient than traditional heating methods (like burning firewood or charcoal). Give reason(s) to support this statement considering societal impact.
Answer:
Electrical heating devices are more convenient than traditional heating methods because:
(i) They do not produce smoke or harmful gases, thus keeping the environment clean.
(ii) They can be easily turned on or off, and the heat can be controlled.
(iii) They help reduce the cutting of trees for firewood and save forests.
7. Look at the Fig. 4.4a. If the compass placed near the coil deflects:
(i) Draw an arrow on the diagram to show the path of the electric current.
(ii) Explain why the compass needle moves when current flows.
(iii) Predict what would happen to the deflection if you reverse the battery terminals.
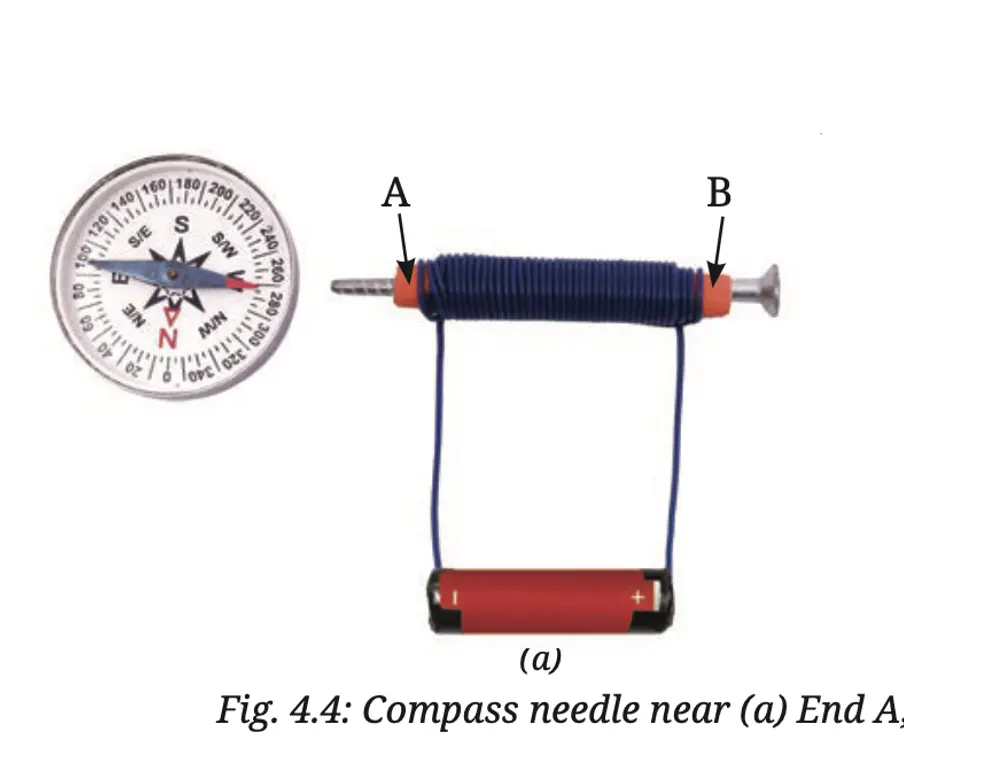
Answer:
(i)
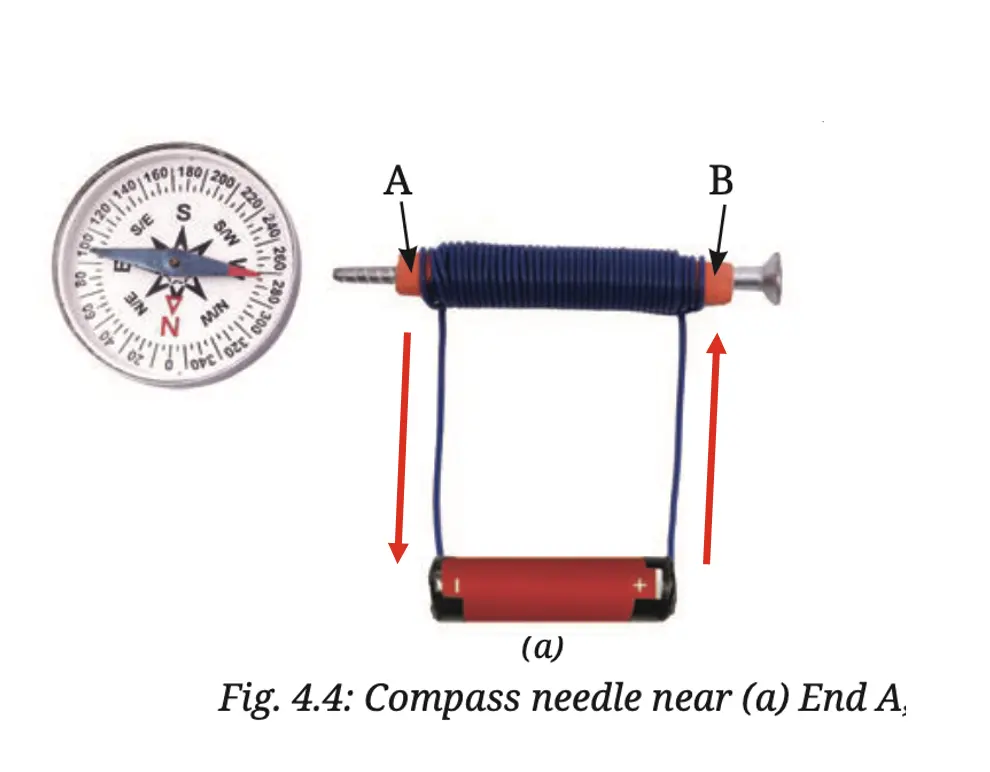
Path of electric current: The current flows from the positive terminal of the cell to end B, passes through the coil from B to A and then returns to the negative terminal of the cell.
(ii) When the current flows through the coil, it behaves like an electromagnet and produces a magnetic field around it. This magnetic field deflects the compass needle.
(iii) On reversing the battery terminals, the direction of the current in the coil is reversed. As a result, the polarity of the coil’s magnetic field also reverses, and the compass needle deflects in the opposite direction.
8. Suppose Sumana forgets to move the switch of her lifting electromagnet model to OFF position (in introduction story). After some time, the iron nail no longer picks up the iron paper clips, but the wire wrapped around the iron nail is still warm. Why did the lifting electromagnet stop lifting the clips? Give possible reasons.
Answer:
A lifting electromagnet works only when current flows through it. Since Sumana forgot to switch her electromagnet model to the OFF position, current kept flowing through the coil for a long time. This continuous passage of current made the wire around the iron nail warm and gradually weakened the cell. Finally, the cell ran out of charge, and the electromagnet stopped picking up the paper clips.
Another possible reason is that the iron nail became too hot due to the heating of the wire. When iron is heated, it loses its magnetic strength temporarily, so the electromagnet could no longer lift the clips.
9. In Fig. 4.11, in which case the LED will glow when the switch is closed?
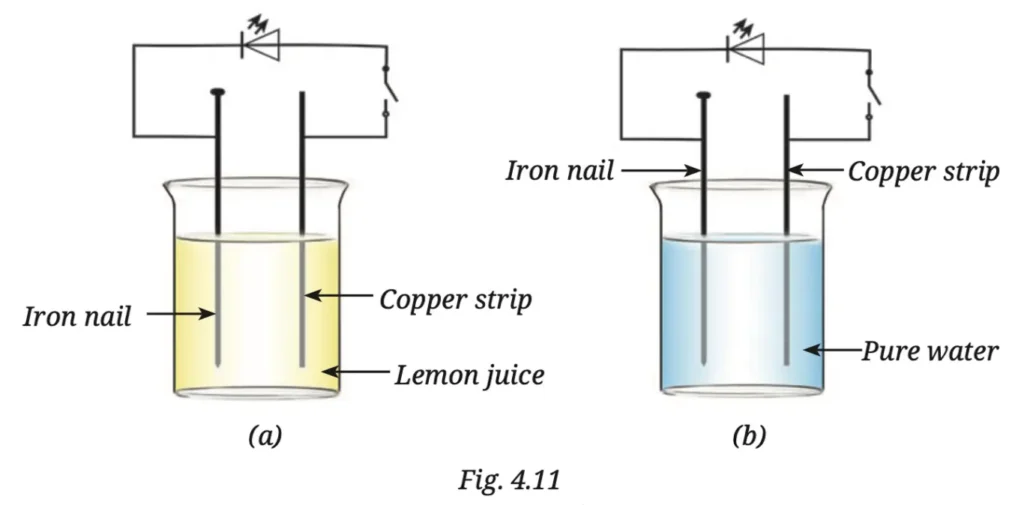
Answer:
An electrolyte in a cell is usually an acid, or salt solution. In case (a), lemon juice is a weak acid and a good conductor of electricity. Therefore, a chemical reaction takes place between the electrodes (iron nail and copper strip), allowing current to flow, and the LED glows.
In case (b), pure water is a very poor conductor of electricity. Since it is not a good electrolyte, no current flows, so the LED does not glow.
10. Neha keeps the coil exactly the same as in Activity 4.4 but slides the iron nail out, leaving only the coiled wire. Will the coil still deflect the compass? If yes, will the deflection be more or less than before?
Answer:
Yes. When the iron nail is removed, the coil alone will still produce a magnetic field and cause the compass needle to deflect. However, the deflection will be less than when the iron nail is inside the coil. This is because inserting the iron nail in the core makes the electromagnet much stronger, leading to greater deflection of the compass needle.
11. We have four coils, of similar shape and size, made up from iron, copper, aluminium, and nichrome as shown in Fig. 4.12.
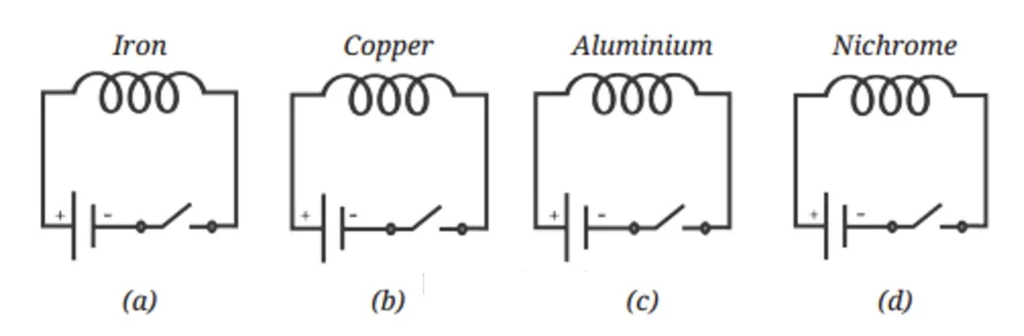
When current is passed through the coils, compass needles placed near the coils will show deflection.
(i) Only in circuit (a)
(ii) Only in circuits (a) and (b)
(iii) Only in circuits (a), (b), and (c)
(iv) In all four circuits
Answer:
The compass needle will show deflection in all four circuits.
However, the amount of deflection will not be the same. It depends on the resistance of the coils used in the circuits. The coil with the least resistance allows the maximum current to flow and produces the greatest deflection, while the coil with higher resistance allows less current and produces smaller deflection.
